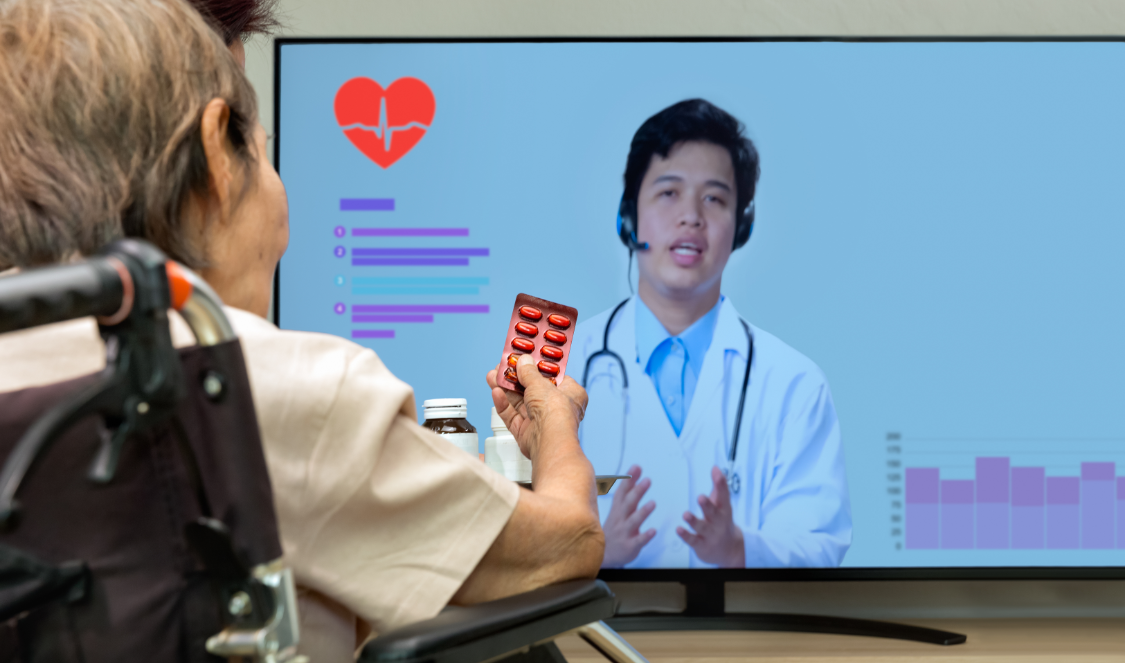
Our exploration of the transformative power of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in telehealth. This blog post will delve into the profound impact AI has on telehealth services, particularly in the areas of remote patient monitoring and population health risk prediction. As we navigate through the digital age, AI has become a pivotal tool in healthcare, enhancing service delivery, improving patient outcomes, and revolutionizing the way we predict health risks.
Understanding Telehealth
Telehealth refers to the use of digital information and communication technologies, such as computers and mobile devices, to access and manage healthcare services remotely. These services can range from virtual doctor consultations and remote patient monitoring to health education services.
Over the years, telehealth has evolved significantly, driven by advancements in technology and the increasing need for accessible healthcare. Today, telehealth is not just a service, but a vital part of the healthcare infrastructure, bridging the gap between patients and healthcare services, especially in remote areas.
The Role of AI in Telehealth
Artificial Intelligence plays a crucial role in telehealth, offering capabilities that extend beyond human intelligence. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and make predictions, all in real-time. This has significant implications for telehealth, improving service delivery and patient outcomes.
For instance, AI can enhance remote patient monitoring by providing real-time analysis of health data, enabling early detection of potential health issues and timely intervention. AI can also help predict population health risks by analyzing patterns in large health datasets, thereby enabling proactive healthcare interventions.
Real-World Examples of AI Applications in Telehealth
AI’s impact on telehealth is not just theoretical, it’s already being felt in real-world applications. For example, AI-powered chatbots are being used to provide instant responses to patient queries, improving patient engagement and satisfaction. In remote patient monitoring, AI algorithms are being used to analyze patient data in real-time, enabling healthcare providers to monitor patient health and intervene promptly when anomalies are detected.
In population health risk prediction, AI models are being used to analyze large datasets and identify risk factors for various diseases. This information can be used to inform public health interventions and strategies, ultimately improving population health outcomes. As we continue to explore the intersection of AI and telehealth, it’s clear that the potential for transformation is immense. Stay tuned as we delve deeper into this exciting topic in the sections to come.
AI and Remote Patient Monitoring
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is playing a transformative role in the field of remote patient monitoring. Remote patient monitoring involves the collection, transmission, evaluation, and communication of patient health data from electronic devices. These devices include wearable sensors, implanted equipment, or other devices that allow remote patient monitoring for chronic diseases.
AI enhances this process by providing real-time analysis and interpretation of health data. For instance, AI algorithms can analyze data from heart rate monitors to detect irregular heart rhythms or potential signs of conditions like atrial fibrillation. Similarly, AI can analyze data from glucose monitors to help manage diabetes, or from wearable devices to monitor vital signs and detect anomalies.
AI in Population Health Risk Prediction
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is playing a transformative role in the field of remote patient monitoring. Remote patient monitoring involves the collection, transmission, evaluation, and communication of patient health data from electronic devices. These devices include wearable sensors, implanted equipment, or other devices that allow remote patient monitoring for chronic diseases.
AI is also making significant strides in population health risk prediction. It involves predicting the probability of certain health outcomes within a population based on a wide range of factors. These factors can include social determinants of health, such as socioeconomic status, education level, and physical environment, along with clinical data.
AI algorithms can analyze these vast and diverse data sets to identify patterns and trends, predict health risks, and inform intervention strategies. For instance, AI can be used to predict the risk of chronic diseases like diabetes or heart disease within a population, helping healthcare providers and policymakers to implement preventative measures.
Discussion on the Effectiveness of AI in Predicting Health Risks
The effectiveness of AI in predicting health risks is evident in its wide-ranging applications. For instance, a study published in Nature Medicine demonstrated that an AI model could predict the risk of cardiovascular death based on retinal images. Another study in the Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association showed that AI could predict the risk of chronic kidney disease.
However, it’s important to note that while AI holds great promise in healthcare, challenges remain. These include issues related to data privacy and security, the need for diverse and representative data to avoid bias in AI predictions, and the ethical considerations of AI decision-making in healthcare.
The Role of AI in Telemedicine
Telemedicine, the practice of medicine across different locations through information and communication technologies, has the potential to be significantly enhanced by the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI). The addition of AI can expand and improve telemedicine capabilities, opening up endless possibilities for developing tailored solutions to meet specific healthcare needs. AI in telemedicine can make a valuable contribution to implementing the healthcare continuum and promoting greater access to integrated care, wherever and whenever necessary.
Case Studies Showcasing the Impact of AI on Remote Patient Monitoring
Cardiogram’s DeepHeart: Cardiogram, a digital health startup, developed an AI-based algorithm called DeepHeart. Using data from wearable devices, DeepHeart can detect diabetes, sleep apnea, hypertension, and atrial fibrillation with high accuracy.
Current Health’s AI-powered Remote Patient Monitoring: Current Health uses AI to analyze data from its wearable device, which monitors vital signs in real-time. The AI algorithm can predict if a patient’s condition is deteriorating and alert healthcare providers.
Emerging Trends in AI-Powered Telemedicine
The potential impact of AI in telemedicine can be identified around four emerging trends
-
-
Patient Monitoring: AI algorithms can monitor patients’ health status remotely in real-time, providing continuous updates to healthcare providers.Healthcare Information Technology: AI can enhance the management and analysis of healthcare data, improving decision-making processes for both providers and patients.
-
-
-
Intelligent Assistance and Diagnosis: AI systems can assist in diagnosing diseases, predicting patient outcomes, and suggesting personalized treatment plans based on a patient’s unique circumstances.
-
-
-
Information Analysis Collaboration: AI can facilitate collaboration among healthcare professionals by providing a platform for securely sharing and collectively analyzing patient data.
-
Overcoming Challenges in AI-Powered Telemedicine
Despite the potential benefits, the implementation of AI in telemedicine faces challenges related to safety, ethics, efficacy, efficiency, regulatory compliance, and financial concerns. Widespread adoption of AI in healthcare will increase if physicians serve as knowledgeable and supportive guides and leaders throughout the process.
AI in Clinical Trials
In addition to telemedicine, AI is also being used to accelerate various stages of the clinical trial process. From study design to patient recruitment, researchers are investigating ways that AI technology could speed up and improve these traditionally time-consuming and costly endeavors.
AI has already demonstrated its value in the early stages of drug discovery, assisting in identifying suitable disease targets and designing new molecule structures. Now, scientists are starting to leverage AI to manage clinical trials more efficiently, including tasks such as writing protocols, recruiting participants, and analyzing data.
The Future of AI in Telemedicine
Looking ahead, AI-powered telemedicine models are actively being developed and tested in various healthcare scenarios. The goal of these innovative models is to improve health outcomes, enhance patient experiences, and reduce the need for in-person visits. As AI and telemedicine technologies continue to evolve in tandem, we can expect to see even more groundbreaking applications emerge that redefine how virtual care is delivered.
Redefining Remote Patient Care
Imagine a world where your health could be monitored continuously, without ever stepping foot in a doctor’s office. AI-powered telemedicine solutions are making this a reality. Sophisticated algorithms can analyze data from wearable devices, implants, and other connected health technologies, providing real-time insights into a patient’s health status. These insights are then relayed to healthcare providers, allowing them to intervene and prevent potential health issues before they escalate proactively.
The Rise of the Virtual Clinician
Beyond just monitoring, AI is also transforming the way diagnoses are made and treatment plans are developed. AI-driven systems can sift through vast amounts of medical data, identify patterns, and suggest personalized treatment options tailored to each patient’s unique circumstances. These virtual clinicians can assist human healthcare professionals, providing valuable insights and recommendations to support decision-making processes.
Collaborative Care, Powered by AI
Telemedicine has traditionally been a one-to-one interaction between a patient and a single provider. However, AI is breaking down these barriers, enabling seamless collaboration among entire healthcare teams. Secure platforms powered by AI can facilitate the sharing and collective analysis of patient data, fostering a more integrated approach to care coordination and delivery.
Accelerating Clinical Research
Beyond direct patient care, AI is also making waves in the realm of clinical research and drug development. Researchers are leveraging AI to streamline various stages of the clinical trial process, from study design and patient recruitment to data analysis. AI algorithms can identify suitable disease targets, design new molecular structures, and even manage the complex logistics of running clinical trials – ultimately accelerating the pace of medical breakthroughs.
The Future of Healthcare, Virtually Reimagined
As AI-powered telemedicine models continue to be developed and tested in real-world healthcare scenarios, we can expect to witness a transformation in how virtual care is delivered. Improved health outcomes, enhanced patient experiences, and reduced in-person visits are just the beginning. The future of healthcare is being virtually reimagined, one AI-driven innovation at a time.
While the integration of AI in telemedicine holds immense potential, it is not without its challenges. Concerns surrounding data privacy, ethical considerations, regulatory compliance, and the need for diverse and representative data must be addressed. However, with physicians and healthcare leaders embracing their role as guides and champions of these cutting-edge technologies, the path towards a future where AI and telemedicine seamlessly intersect becomes increasingly clear.
Leading telehealth application in the medical field
Healee: A Versatile Telemedicine Solution
Healee stands out as a reliable and flexible telemedicine platform tailored to support multi-party virtual consultations. This innovative solution enables seamless collaboration among multidisciplinary healthcare teams, facilitating coordinated patient care. Designed with real-world clinical workflows in mind, Healee prioritizes factors such as reliability, reproducibility, usability, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness. While specific pricing details are not publicly disclosed, Healee’s costs are intended to align with the unique needs of healthcare organizations.
Pros: It provides a good opportunity for vital meetings with patients The software’s interface is very user-friendly.
Cons: Some users have reported issues with installation. There are also comments about the software being too much stuck to traditional medicine and needing more alternative options.
Pabau: Paving the Way for AI-Powered Virtual Care
Pabau offers integrated clinic management software that incorporates a unique AI tool for prescription management and telehealth services. This cutting-edge platform seamlessly blends into existing clinical practices, ensuring a smooth transition to virtual care delivery. Pabau’s design considerations include reliability, reproducibility, usability, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness, ensuring a comprehensive solution tailored to the needs of healthcare providers. Pricing is customized based on the specific requirements of each organization.
Pros: Pabau is very modern and slick-looking. It has plenty of scope to expand and add new features. Users appreciate the automation built into the system.
Cons: Some users have reported that the appointment screen is very dark and would prefer more clinical colors. There have also been reports of downtime and significant lag.
Updox: Streamlining Patient Communication
Updox is a comprehensive patient communication platform that simplifies the exchange of information between healthcare providers and their patients. This all-inclusive solution provides a suite of tools to facilitate effective communication, from appointment reminders to secure messaging. Updox’s design focuses on integrating seamlessly with existing clinical workflows while prioritizing reliability, reproducibility, usability, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness. Customized pricing plans are available to align with the unique requirements of healthcare organizations.
Pros: Updox is easy to use and documents telehealth visits well. It integrates easily with EMR since it already uses fax, email, and text features.
Cons: Some users have reported occasional technical glitches and limited customization options.
Teladoc Health: Global Access to Virtual Care
Teladoc Health is a global healthcare access platform that provides round-the-clock virtual care services. This comprehensive solution enables patients to connect with healthcare providers from anywhere in the world, breaking down geographical barriers to quality care. Teladoc Health’s design considers factors such as reliability, reproducibility, usability, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness, ensuring a seamless virtual care experience. Pricing is tailored to the specific needs of healthcare organizations, enabling widespread access to this innovative platform.
Pros: Teladoc Health offers appointments 24 hours a day, 7 days a week. The copay may be less than an in-person visit. Services are available at a flat rate without insurance.
Cons: There’s no ability to follow up after a general medical visit. The absence of physical examination may limit a doctor’s diagnosis.
Cliniko: Hassle-Free Scheduling and Virtual Visits
Cliniko is a user-friendly scheduling and virtual visit platform designed to streamline the delivery of telehealth services. This hassle-free solution eliminates the complexities often associated with virtual care, making it accessible to both healthcare providers and patients. Cliniko’s design prioritizes reliability, reproducibility, usability, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness, ensuring a smooth and efficient virtual care experience. Customized pricing plans are available to meet the unique needs of healthcare organizations.
Pros: Cliniko is easy to use and navigate. It provides a good service and very good customer service and help.
Cons: Some users have reported that they cannot attach a PDF to an email15. There are also comments about not being able to easily see in the diary that patients have cancelled their appointments.
OhMD: Secure Messaging for Healthcare Professionals
OhMD is a HIPAA-compliant secure messaging platform specifically designed for healthcare providers. This robust solution enables secure and confidential communication among healthcare teams, facilitating seamless collaboration and coordination of care. OhMD’s design considers factors such as reliability, reproducibility, usability, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness, ensuring a secure and efficient communication experience. Pricing is tailored to the specific needs of healthcare organizations, enabling widespread adoption of this secure messaging platform.
Pros: It’s HIPAA secure and so easy for patients and providers to use18. It reduces the amount of phone tag played with patients.
Cons: Some users have reported chronic errors and delays in the importing of documents from OhMD into their actual EMR.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing the field of telehealth by enhancing remote patient monitoring and enabling accurate population health risk prediction. In remote patient monitoring, AI algorithms can analyze data from wearable devices and sensors in real-time, Enabling early detection of potential health issues and timely interventions. Case studies like Cardiogram’s DeepHeart and Current Health’s AI-powered monitoring solutions demonstrate the effectiveness of AI in detecting conditions like atrial fibrillation, sleep apnea, and deteriorating vital signs.
Additionally, AI plays a crucial role in population health risk prediction by analyzing vast and diverse datasets, including clinical data and social determinants of health. AI models can identify patterns and trends, predicting the risk of chronic diseases like diabetes, heart disease, and chronic kidney disease within populations.
Studies published in reputable journals, such as Nature Medicine and the Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association, have shown the effectiveness of AI in predicting health risks based on retinal images and other data sources.
While AI holds immense potential to improve healthcare outcomes through telehealth, challenges remain.
These include concerns over data privacy and security, the need for diverse and representative data to avoid bias in AI predictions, and ethical considerations surrounding AI decision-making in healthcare. Addressing these challenges is crucial to fully realizing the benefits of AI in telehealth.
The integration of AI in telehealth services, particularly in remote patient monitoring and population health risk prediction, is transforming the healthcare landscape, offering more personalized, proactive, and accessible healthcare solutions.
Our exploration of the transformative power of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in telehealth. This blog post will delve into the profound impact AI has on telehealth services, particularly in the areas of remote patient monitoring and population health risk prediction. As we navigate through the digital age, AI has become a pivotal tool in healthcare, enhancing service delivery, improving patient outcomes, and revolutionizing the way we predict health risks.
Understanding Telehealth
Telehealth refers to the use of digital information and communication technologies, such as computers and mobile devices, to access and manage healthcare services remotely. These services can range from virtual doctor consultations and remote patient monitoring to health education services.
Over the years, telehealth has evolved significantly, driven by advancements in technology and the increasing need for accessible healthcare. Today, telehealth is not just a service, but a vital part of the healthcare infrastructure, bridging the gap between patients and healthcare services, especially in remote areas.
The Role of AI in Telehealth
Artificial Intelligence plays a crucial role in telehealth, offering capabilities that extend beyond human intelligence. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and make predictions, all in real-time. This has significant implications for telehealth, improving service delivery and patient outcomes.
For instance, AI can enhance remote patient monitoring by providing real-time analysis of health data, enabling early detection of potential health issues and timely intervention. AI can also help predict population health risks by analyzing patterns in large health datasets, thereby enabling proactive healthcare interventions.
Real-World Examples of AI Applications in Telehealth
AI’s impact on telehealth is not just theoretical, it’s already being felt in real-world applications. For example, AI-powered chatbots are being used to provide instant responses to patient queries, improving patient engagement and satisfaction. In remote patient monitoring, AI algorithms are being used to analyze patient data in real-time, enabling healthcare providers to monitor patient health and intervene promptly when anomalies are detected.
In population health risk prediction, AI models are being used to analyze large datasets and identify risk factors for various diseases. This information can be used to inform public health interventions and strategies, ultimately improving population health outcomes. As we continue to explore the intersection of AI and telehealth, it’s clear that the potential for transformation is immense. Stay tuned as we delve deeper into this exciting topic in the sections to come.
AI and Remote Patient Monitoring
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is playing a transformative role in the field of remote patient monitoring. Remote patient monitoring involves the collection, transmission, evaluation, and communication of patient health data from electronic devices. These devices include wearable sensors, implanted equipment, or other devices that allow remote patient monitoring for chronic diseases.
AI enhances this process by providing real-time analysis and interpretation of health data. For instance, AI algorithms can analyze data from heart rate monitors to detect irregular heart rhythms or potential signs of conditions like atrial fibrillation. Similarly, AI can analyze data from glucose monitors to help manage diabetes, or from wearable devices to monitor vital signs and detect anomalies.
Case Studies Showcasing the Impact of AI on Remote Patient Monitoring
Cardiogram’s DeepHeart: Cardiogram, a digital health startup, developed an AI-based algorithm called DeepHeart. Using data from wearable devices, DeepHeart can detect diabetes, sleep apnea, hypertension, and atrial fibrillation with high accuracy.
Current Health’s AI-powered Remote Patient Monitoring: Current Health uses AI to analyze data from its wearable device, which monitors vital signs in real-time. The AI algorithm can predict if a patient’s condition is deteriorating and alert healthcare providers.
AI in Population Health Risk Prediction
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is playing a transformative role in the field of remote patient monitoring. Remote patient monitoring involves the collection, transmission, evaluation, and communication of patient health data from electronic devices. These devices include wearable sensors, implanted equipment, or other devices that allow remote patient monitoring for chronic diseases.
AI is also making significant strides in population health risk prediction. It involves predicting the probability of certain health outcomes within a population based on a wide range of factors. These factors can include social determinants of health, such as socioeconomic status, education level, and physical environment, along with clinical data.
AI algorithms can analyze these vast and diverse data sets to identify patterns and trends, predict health risks, and inform intervention strategies. For instance, AI can be used to predict the risk of chronic diseases like diabetes or heart disease within a population, helping healthcare providers and policymakers to implement preventative measures.
Discussion on the Effectiveness of AI in Predicting Health Risks
The effectiveness of AI in predicting health risks is evident in its wide-ranging applications. For instance, a study published in Nature Medicine demonstrated that an AI model could predict the risk of cardiovascular death based on retinal images. Another study in the Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association showed that AI could predict the risk of chronic kidney disease.
However, it’s important to note that while AI holds great promise in healthcare, challenges remain. These include issues related to data privacy and security, the need for diverse and representative data to avoid bias in AI predictions, and the ethical considerations of AI decision-making in healthcare.
The Role of AI in Telemedicine
Telemedicine, the practice of medicine across different locations through information and communication technologies, has the potential to be significantly enhanced by the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI). The addition of AI can expand and improve telemedicine capabilities, opening up endless possibilities for developing tailored solutions to meet specific healthcare needs. AI in telemedicine can make a valuable contribution to implementing the healthcare continuum and promoting greater access to integrated care, wherever and whenever necessary.
Emerging Trends in AI-Powered Telemedicine
The potential impact of AI in telemedicine can be identified around four emerging trends
-
-
Patient Monitoring: AI algorithms can monitor patients’ health status remotely in real-time, providing continuous updates to healthcare providers.Healthcare Information Technology: AI can enhance the management and analysis of healthcare data, improving decision-making processes for both providers and patients.
-
-
-
Intelligent Assistance and Diagnosis: AI systems can assist in diagnosing diseases, predicting patient outcomes, and suggesting personalized treatment plans based on a patient’s unique circumstances.
-
-
-
Information Analysis Collaboration: AI can facilitate collaboration among healthcare professionals by providing a platform for securely sharing and collectively analyzing patient data.
-
Overcoming Challenges in AI-Powered Telemedicine
Despite the potential benefits, the implementation of AI in telemedicine faces challenges related to safety, ethics, efficacy, efficiency, regulatory compliance, and financial concerns. Widespread adoption of AI in healthcare will increase if physicians serve as knowledgeable and supportive guides and leaders throughout the process.
AI in Clinical Trials
In addition to telemedicine, AI is also being used to accelerate various stages of the clinical trial process. From study design to patient recruitment, researchers are investigating ways that AI technology could speed up and improve these traditionally time-consuming and costly endeavors.
AI has already demonstrated its value in the early stages of drug discovery, assisting in identifying suitable disease targets and designing new molecule structures. Now, scientists are starting to leverage AI to manage clinical trials more efficiently, including tasks such as writing protocols, recruiting participants, and analyzing data.
The Future of AI in Telemedicine
Looking ahead, AI-powered telemedicine models are actively being developed and tested in various healthcare scenarios. The goal of these innovative models is to improve health outcomes, enhance patient experiences, and reduce the need for in-person visits. As AI and telemedicine technologies continue to evolve in tandem, we can expect to see even more groundbreaking applications emerge that redefine how virtual care is delivered.
Redefining Remote Patient Care
Imagine a world where your health could be monitored continuously, without ever stepping foot in a doctor’s office. AI-powered telemedicine solutions are making this a reality. Sophisticated algorithms can analyze data from wearable devices, implants, and other connected health technologies, providing real-time insights into a patient’s health status. These insights are then relayed to healthcare providers, allowing them to intervene and prevent potential health issues before they escalate proactively.
The Rise of the Virtual Clinician
Beyond just monitoring, AI is also transforming the way diagnoses are made and treatment plans are developed. AI-driven systems can sift through vast amounts of medical data, identify patterns, and suggest personalized treatment options tailored to each patient’s unique circumstances. These virtual clinicians can assist human healthcare professionals, providing valuable insights and recommendations to support decision-making processes.
Collaborative Care, Powered by AI
Telemedicine has traditionally been a one-to-one interaction between a patient and a single provider. However, AI is breaking down these barriers, enabling seamless collaboration among entire healthcare teams. Secure platforms powered by AI can facilitate the sharing and collective analysis of patient data, fostering a more integrated approach to care coordination and delivery.
Accelerating Clinical Research
Beyond direct patient care, AI is also making waves in the realm of clinical research and drug development. Researchers are leveraging AI to streamline various stages of the clinical trial process, from study design and patient recruitment to data analysis. AI algorithms can identify suitable disease targets, design new molecular structures, and even manage the complex logistics of running clinical trials – ultimately accelerating the pace of medical breakthroughs.
The Future of Healthcare, Virtually Reimagined
As AI-powered telemedicine models continue to be developed and tested in real-world healthcare scenarios, we can expect to witness a transformation in how virtual care is delivered. Improved health outcomes, enhanced patient experiences, and reduced in-person visits are just the beginning. The future of healthcare is being virtually reimagined, one AI-driven innovation at a time.
While the integration of AI in telemedicine holds immense potential, it is not without its challenges. Concerns surrounding data privacy, ethical considerations, regulatory compliance, and the need for diverse and representative data must be addressed. However, with physicians and healthcare leaders embracing their role as guides and champions of these cutting-edge technologies, the path towards a future where AI and telemedicine seamlessly intersect becomes increasingly clear.
Leading telehealth application in the medical field
Healee: A Versatile Telemedicine Solution
Healee stands out as a reliable and flexible telemedicine platform tailored to support multi-party virtual consultations. This innovative solution enables seamless collaboration among multidisciplinary healthcare teams, facilitating coordinated patient care. Designed with real-world clinical workflows in mind, Healee prioritizes factors such as reliability, reproducibility, usability, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness. While specific pricing details are not publicly disclosed, Healee’s costs are intended to align with the unique needs of healthcare organizations.
Pros: It provides a good opportunity for vital meetings with patients The software’s interface is very user-friendly.
Cons: Some users have reported issues with installation. There are also comments about the software being too much stuck to traditional medicine and needing more alternative options.
Pabau: Paving the Way for AI-Powered Virtual Care
Pabau offers integrated clinic management software that incorporates a unique AI tool for prescription management and telehealth services. This cutting-edge platform seamlessly blends into existing clinical practices, ensuring a smooth transition to virtual care delivery. Pabau’s design considerations include reliability, reproducibility, usability, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness, ensuring a comprehensive solution tailored to the needs of healthcare providers. Pricing is customized based on the specific requirements of each organization.
Pros: Pabau is very modern and slick-looking. It has plenty of scope to expand and add new features. Users appreciate the automation built into the system.
Cons: Some users have reported that the appointment screen is very dark and would prefer more clinical colors. There have also been reports of downtime and significant lag.
Updox: Streamlining Patient Communication
Updox is a comprehensive patient communication platform that simplifies the exchange of information between healthcare providers and their patients. This all-inclusive solution provides a suite of tools to facilitate effective communication, from appointment reminders to secure messaging. Updox’s design focuses on integrating seamlessly with existing clinical workflows while prioritizing reliability, reproducibility, usability, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness. Customized pricing plans are available to align with the unique requirements of healthcare organizations.
Pros: Updox is easy to use and documents telehealth visits well. It integrates easily with EMR since it already uses fax, email, and text features.
Cons: Some users have reported occasional technical glitches and limited customization options.
Teladoc Health: Global Access to Virtual Care
Teladoc Health is a global healthcare access platform that provides round-the-clock virtual care services. This comprehensive solution enables patients to connect with healthcare providers from anywhere in the world, breaking down geographical barriers to quality care. Teladoc Health’s design considers factors such as reliability, reproducibility, usability, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness, ensuring a seamless virtual care experience. Pricing is tailored to the specific needs of healthcare organizations, enabling widespread access to this innovative platform.
Pros: Teladoc Health offers appointments 24 hours a day, 7 days a week. The copay may be less than an in-person visit. Services are available at a flat rate without insurance.
Cons: There’s no ability to follow up after a general medical visit. The absence of physical examination may limit a doctor’s diagnosis.
Cliniko: Hassle-Free Scheduling and Virtual Visits
Cliniko is a user-friendly scheduling and virtual visit platform designed to streamline the delivery of telehealth services. This hassle-free solution eliminates the complexities often associated with virtual care, making it accessible to both healthcare providers and patients. Cliniko’s design prioritizes reliability, reproducibility, usability, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness, ensuring a smooth and efficient virtual care experience. Customized pricing plans are available to meet the unique needs of healthcare organizations.
Pros: Cliniko is easy to use and navigate. It provides a good service and very good customer service and help.
Cons: Some users have reported that they cannot attach a PDF to an email15. There are also comments about not being able to easily see in the diary that patients have cancelled their appointments.
OhMD: Secure Messaging for Healthcare Professionals
OhMD is a HIPAA-compliant secure messaging platform specifically designed for healthcare providers. This robust solution enables secure and confidential communication among healthcare teams, facilitating seamless collaboration and coordination of care. OhMD’s design considers factors such as reliability, reproducibility, usability, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness, ensuring a secure and efficient communication experience. Pricing is tailored to the specific needs of healthcare organizations, enabling widespread adoption of this secure messaging platform.
Pros: It’s HIPAA secure and so easy for patients and providers to use18. It reduces the amount of phone tag played with patients.
Cons: Some users have reported chronic errors and delays in the importing of documents from OhMD into their actual EMR.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing the field of telehealth by enhancing remote patient monitoring and enabling accurate population health risk prediction. In remote patient monitoring, AI algorithms can analyze data from wearable devices and sensors in real-time, Enabling early detection of potential health issues and timely interventions. Case studies like Cardiogram’s DeepHeart and Current Health’s AI-powered monitoring solutions demonstrate the effectiveness of AI in detecting conditions like atrial fibrillation, sleep apnea, and deteriorating vital signs.
Additionally, AI plays a crucial role in population health risk prediction by analyzing vast and diverse datasets, including clinical data and social determinants of health. AI models can identify patterns and trends, predicting the risk of chronic diseases like diabetes, heart disease, and chronic kidney disease within populations.
Studies published in reputable journals, such as Nature Medicine and the Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association, have shown the effectiveness of AI in predicting health risks based on retinal images and other data sources.
While AI holds immense potential to improve healthcare outcomes through telehealth, challenges remain.
These include concerns over data privacy and security, the need for diverse and representative data to avoid bias in AI predictions, and ethical considerations surrounding AI decision-making in healthcare. Addressing these challenges is crucial to fully realizing the benefits of AI in telehealth.
The integration of AI in telehealth services, particularly in remote patient monitoring and population health risk prediction, is transforming the healthcare landscape, offering more personalized, proactive, and accessible healthcare solutions.
Our exploration of the transformative power of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in telehealth. This blog post will delve into the profound impact AI has on telehealth services, particularly in the areas of remote patient monitoring and population health risk prediction. As we navigate through the digital age, AI has become a pivotal tool in healthcare, enhancing service delivery, improving patient outcomes, and revolutionizing the way we predict health risks.
Understanding Telehealth
Telehealth refers to the use of digital information and communication technologies, such as computers and mobile devices, to access and manage healthcare services remotely. These services can range from virtual doctor consultations and remote patient monitoring to health education services.
Over the years, telehealth has evolved significantly, driven by advancements in technology and the increasing need for accessible healthcare. Today, telehealth is not just a service, but a vital part of the healthcare infrastructure, bridging the gap between patients and healthcare services, especially in remote areas.
The Role of AI in Telehealth
Artificial Intelligence plays a crucial role in telehealth, offering capabilities that extend beyond human intelligence. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and make predictions, all in real-time. This has significant implications for telehealth, improving service delivery and patient outcomes.
For instance, AI can enhance remote patient monitoring by providing real-time analysis of health data, enabling early detection of potential health issues and timely intervention. AI can also help predict population health risks by analyzing patterns in large health datasets, thereby enabling proactive healthcare interventions.
Real-World Examples of AI Applications in Telehealth
AI’s impact on telehealth is not just theoretical, it’s already being felt in real-world applications. For example, AI-powered chatbots are being used to provide instant responses to patient queries, improving patient engagement and satisfaction. In remote patient monitoring, AI algorithms are being used to analyze patient data in real-time, enabling healthcare providers to monitor patient health and intervene promptly when anomalies are detected.
In population health risk prediction, AI models are being used to analyze large datasets and identify risk factors for various diseases. This information can be used to inform public health interventions and strategies, ultimately improving population health outcomes. As we continue to explore the intersection of AI and telehealth, it’s clear that the potential for transformation is immense. Stay tuned as we delve deeper into this exciting topic in the sections to come.
AI and Remote Patient Monitoring
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is playing a transformative role in the field of remote patient monitoring. Remote patient monitoring involves the collection, transmission, evaluation, and communication of patient health data from electronic devices. These devices include wearable sensors, implanted equipment, or other devices that allow remote patient monitoring for chronic diseases.
AI enhances this process by providing real-time analysis and interpretation of health data. For instance, AI algorithms can analyze data from heart rate monitors to detect irregular heart rhythms or potential signs of conditions like atrial fibrillation. Similarly, AI can analyze data from glucose monitors to help manage diabetes, or from wearable devices to monitor vital signs and detect anomalies.
Case Studies Showcasing the Impact of AI on Remote Patient Monitoring
Cardiogram’s DeepHeart: Cardiogram, a digital health startup, developed an AI-based algorithm called DeepHeart. Using data from wearable devices, DeepHeart can detect diabetes, sleep apnea, hypertension, and atrial fibrillation with high accuracy.
Current Health’s AI-powered Remote Patient Monitoring: Current Health uses AI to analyze data from its wearable device, which monitors vital signs in real-time. The AI algorithm can predict if a patient’s condition is deteriorating and alert healthcare providers.
AI in Population Health Risk Prediction
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is playing a transformative role in the field of remote patient monitoring. Remote patient monitoring involves the collection, transmission, evaluation, and communication of patient health data from electronic devices. These devices include wearable sensors, implanted equipment, or other devices that allow remote patient monitoring for chronic diseases.
AI is also making significant strides in population health risk prediction. It involves predicting the probability of certain health outcomes within a population based on a wide range of factors. These factors can include social determinants of health, such as socioeconomic status, education level, and physical environment, along with clinical data.
AI algorithms can analyze these vast and diverse data sets to identify patterns and trends, predict health risks, and inform intervention strategies. For instance, AI can be used to predict the risk of chronic diseases like diabetes or heart disease within a population, helping healthcare providers and policymakers to implement preventative measures.
Discussion on the Effectiveness of AI in Predicting Health Risks
The effectiveness of AI in predicting health risks is evident in its wide-ranging applications. For instance, a study published in Nature Medicine demonstrated that an AI model could predict the risk of cardiovascular death based on retinal images. Another study in the Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association showed that AI could predict the risk of chronic kidney disease.
However, it’s important to note that while AI holds great promise in healthcare, challenges remain. These include issues related to data privacy and security, the need for diverse and representative data to avoid bias in AI predictions, and the ethical considerations of AI decision-making in healthcare.
The Role of AI in Telemedicine
Telemedicine, the practice of medicine across different locations through information and communication technologies, has the potential to be significantly enhanced by the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI). The addition of AI can expand and improve telemedicine capabilities, opening up endless possibilities for developing tailored solutions to meet specific healthcare needs. AI in telemedicine can make a valuable contribution to implementing the healthcare continuum and promoting greater access to integrated care, wherever and whenever necessary.
Emerging Trends in AI-Powered Telemedicine
The potential impact of AI in telemedicine can be identified around four emerging trends
-
-
Patient Monitoring: AI algorithms can monitor patients’ health status remotely in real-time, providing continuous updates to healthcare providers.Healthcare Information Technology: AI can enhance the management and analysis of healthcare data, improving decision-making processes for both providers and patients.
-
-
-
Intelligent Assistance and Diagnosis: AI systems can assist in diagnosing diseases, predicting patient outcomes, and suggesting personalized treatment plans based on a patient’s unique circumstances.
-
-
-
Information Analysis Collaboration: AI can facilitate collaboration among healthcare professionals by providing a platform for securely sharing and collectively analyzing patient data.
-
Overcoming Challenges in AI-Powered Telemedicine
Despite the potential benefits, the implementation of AI in telemedicine faces challenges related to safety, ethics, efficacy, efficiency, regulatory compliance, and financial concerns. Widespread adoption of AI in healthcare will increase if physicians serve as knowledgeable and supportive guides and leaders throughout the process.
AI in Clinical Trials
In addition to telemedicine, AI is also being used to accelerate various stages of the clinical trial process. From study design to patient recruitment, researchers are investigating ways that AI technology could speed up and improve these traditionally time-consuming and costly endeavors.
AI has already demonstrated its value in the early stages of drug discovery, assisting in identifying suitable disease targets and designing new molecule structures. Now, scientists are starting to leverage AI to manage clinical trials more efficiently, including tasks such as writing protocols, recruiting participants, and analyzing data.
The Future of AI in Telemedicine
Looking ahead, AI-powered telemedicine models are actively being developed and tested in various healthcare scenarios. The goal of these innovative models is to improve health outcomes, enhance patient experiences, and reduce the need for in-person visits. As AI and telemedicine technologies continue to evolve in tandem, we can expect to see even more groundbreaking applications emerge that redefine how virtual care is delivered.
Redefining Remote Patient Care
Imagine a world where your health could be monitored continuously, without ever stepping foot in a doctor’s office. AI-powered telemedicine solutions are making this a reality. Sophisticated algorithms can analyze data from wearable devices, implants, and other connected health technologies, providing real-time insights into a patient’s health status. These insights are then relayed to healthcare providers, allowing them to intervene and prevent potential health issues before they escalate proactively.
The Rise of the Virtual Clinician
Beyond just monitoring, AI is also transforming the way diagnoses are made and treatment plans are developed. AI-driven systems can sift through vast amounts of medical data, identify patterns, and suggest personalized treatment options tailored to each patient’s unique circumstances. These virtual clinicians can assist human healthcare professionals, providing valuable insights and recommendations to support decision-making processes.
Collaborative Care, Powered by AI
Telemedicine has traditionally been a one-to-one interaction between a patient and a single provider. However, AI is breaking down these barriers, enabling seamless collaboration among entire healthcare teams. Secure platforms powered by AI can facilitate the sharing and collective analysis of patient data, fostering a more integrated approach to care coordination and delivery.
Accelerating Clinical Research
Beyond direct patient care, AI is also making waves in the realm of clinical research and drug development. Researchers are leveraging AI to streamline various stages of the clinical trial process, from study design and patient recruitment to data analysis. AI algorithms can identify suitable disease targets, design new molecular structures, and even manage the complex logistics of running clinical trials – ultimately accelerating the pace of medical breakthroughs.
The Future of Healthcare, Virtually Reimagined
As AI-powered telemedicine models continue to be developed and tested in real-world healthcare scenarios, we can expect to witness a transformation in how virtual care is delivered. Improved health outcomes, enhanced patient experiences, and reduced in-person visits are just the beginning. The future of healthcare is being virtually reimagined, one AI-driven innovation at a time.
While the integration of AI in telemedicine holds immense potential, it is not without its challenges. Concerns surrounding data privacy, ethical considerations, regulatory compliance, and the need for diverse and representative data must be addressed. However, with physicians and healthcare leaders embracing their role as guides and champions of these cutting-edge technologies, the path towards a future where AI and telemedicine seamlessly intersect becomes increasingly clear.
Leading telehealth application in the medical field
Healee: A Versatile Telemedicine Solution
Healee stands out as a reliable and flexible telemedicine platform tailored to support multi-party virtual consultations. This innovative solution enables seamless collaboration among multidisciplinary healthcare teams, facilitating coordinated patient care. Designed with real-world clinical workflows in mind, Healee prioritizes factors such as reliability, reproducibility, usability, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness. While specific pricing details are not publicly disclosed, Healee’s costs are intended to align with the unique needs of healthcare organizations.
Pros: It provides a good opportunity for vital meetings with patients The software’s interface is very user-friendly.
Cons: Some users have reported issues with installation. There are also comments about the software being too much stuck to traditional medicine and needing more alternative options.
Pabau: Paving the Way for AI-Powered Virtual Care
Pabau offers integrated clinic management software that incorporates a unique AI tool for prescription management and telehealth services. This cutting-edge platform seamlessly blends into existing clinical practices, ensuring a smooth transition to virtual care delivery. Pabau’s design considerations include reliability, reproducibility, usability, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness, ensuring a comprehensive solution tailored to the needs of healthcare providers. Pricing is customized based on the specific requirements of each organization.
Pros: Pabau is very modern and slick-looking. It has plenty of scope to expand and add new features. Users appreciate the automation built into the system.
Cons: Some users have reported that the appointment screen is very dark and would prefer more clinical colors. There have also been reports of downtime and significant lag.
Updox: Streamlining Patient Communication
Updox is a comprehensive patient communication platform that simplifies the exchange of information between healthcare providers and their patients. This all-inclusive solution provides a suite of tools to facilitate effective communication, from appointment reminders to secure messaging. Updox’s design focuses on integrating seamlessly with existing clinical workflows while prioritizing reliability, reproducibility, usability, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness. Customized pricing plans are available to align with the unique requirements of healthcare organizations.
Pros: Updox is easy to use and documents telehealth visits well. It integrates easily with EMR since it already uses fax, email, and text features.
Cons: Some users have reported occasional technical glitches and limited customization options.
Teladoc Health: Global Access to Virtual Care
Teladoc Health is a global healthcare access platform that provides round-the-clock virtual care services. This comprehensive solution enables patients to connect with healthcare providers from anywhere in the world, breaking down geographical barriers to quality care. Teladoc Health’s design considers factors such as reliability, reproducibility, usability, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness, ensuring a seamless virtual care experience. Pricing is tailored to the specific needs of healthcare organizations, enabling widespread access to this innovative platform.
Pros: Teladoc Health offers appointments 24 hours a day, 7 days a week. The copay may be less than an in-person visit. Services are available at a flat rate without insurance.
Cons: There’s no ability to follow up after a general medical visit. The absence of physical examination may limit a doctor’s diagnosis.
Cliniko: Hassle-Free Scheduling and Virtual Visits
Cliniko is a user-friendly scheduling and virtual visit platform designed to streamline the delivery of telehealth services. This hassle-free solution eliminates the complexities often associated with virtual care, making it accessible to both healthcare providers and patients. Cliniko’s design prioritizes reliability, reproducibility, usability, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness, ensuring a smooth and efficient virtual care experience. Customized pricing plans are available to meet the unique needs of healthcare organizations.
Pros: Cliniko is easy to use and navigate. It provides a good service and very good customer service and help.
Cons: Some users have reported that they cannot attach a PDF to an email15. There are also comments about not being able to easily see in the diary that patients have cancelled their appointments.
OhMD: Secure Messaging for Healthcare Professionals
OhMD is a HIPAA-compliant secure messaging platform specifically designed for healthcare providers. This robust solution enables secure and confidential communication among healthcare teams, facilitating seamless collaboration and coordination of care. OhMD’s design considers factors such as reliability, reproducibility, usability, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness, ensuring a secure and efficient communication experience. Pricing is tailored to the specific needs of healthcare organizations, enabling widespread adoption of this secure messaging platform.
Pros: It’s HIPAA secure and so easy for patients and providers to use18. It reduces the amount of phone tag played with patients.
Cons: Some users have reported chronic errors and delays in the importing of documents from OhMD into their actual EMR.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing the field of telehealth by enhancing remote patient monitoring and enabling accurate population health risk prediction. In remote patient monitoring, AI algorithms can analyze data from wearable devices and sensors in real-time, Enabling early detection of potential health issues and timely interventions. Case studies like Cardiogram’s DeepHeart and Current Health’s AI-powered monitoring solutions demonstrate the effectiveness of AI in detecting conditions like atrial fibrillation, sleep apnea, and deteriorating vital signs.
Additionally, AI plays a crucial role in population health risk prediction by analyzing vast and diverse datasets, including clinical data and social determinants of health. AI models can identify patterns and trends, predicting the risk of chronic diseases like diabetes, heart disease, and chronic kidney disease within populations.
Studies published in reputable journals, such as Nature Medicine and the Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association, have shown the effectiveness of AI in predicting health risks based on retinal images and other data sources.
While AI holds immense potential to improve healthcare outcomes through telehealth, challenges remain.
These include concerns over data privacy and security, the need for diverse and representative data to avoid bias in AI predictions, and ethical considerations surrounding AI decision-making in healthcare. Addressing these challenges is crucial to fully realizing the benefits of AI in telehealth.
The integration of AI in telehealth services, particularly in remote patient monitoring and population health risk prediction, is transforming the healthcare landscape, offering more personalized, proactive, and accessible healthcare solutions.